SCIENCE
FABRY DISEASE
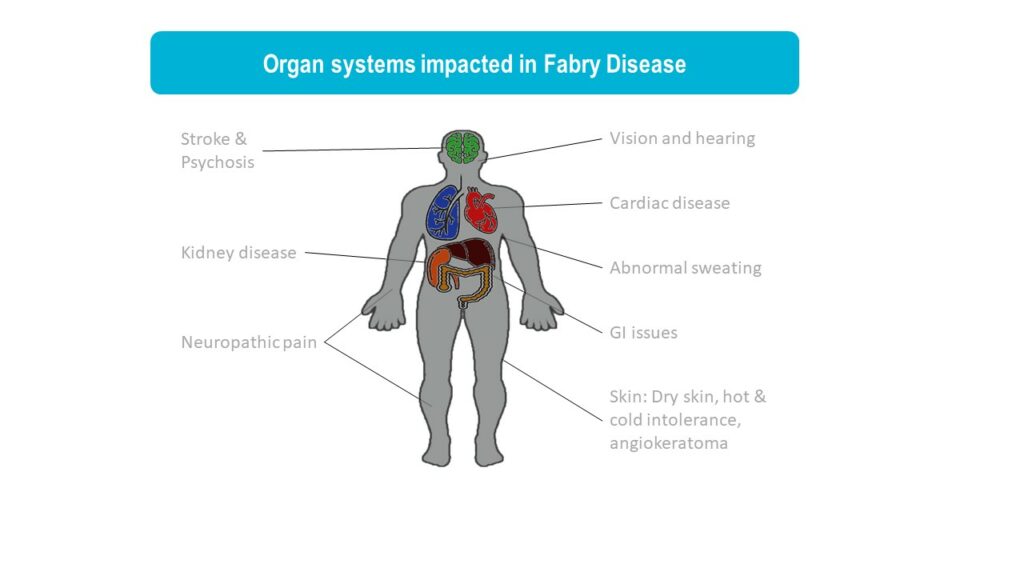
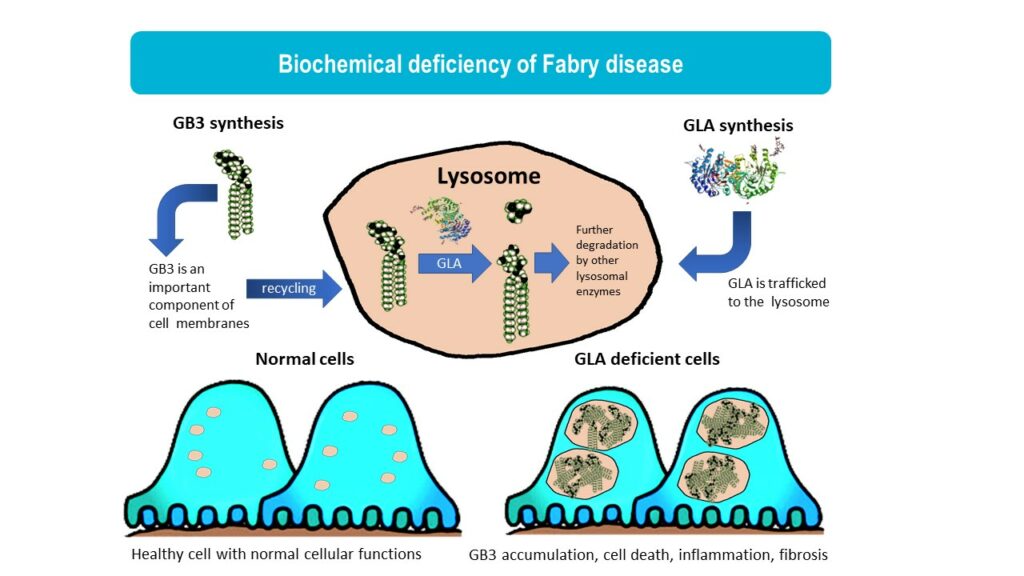
Fabry disease is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the GLA gene, leading to reduced activity of the enzyme a-galactosidase A (GalA). In Fabry disease patients, GalA deficiency results in the accumulation of globotriaosylceramide (GL3), leading to a wide range of symptoms from pain, gastrointestinal issues, eye and skin problems to kidney failure, heart disease, and stroke. Fabry disease is an x-linked disorder and it more commonly seen in males although females can also develop Fabry disease that is usually milder. It is estimated that 1 in 50,000 males are affected by Fabry disease.
Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) is the standard of care for Fabry disease. While ERT reduces progression of many Fabry symptoms, the benefits are incomplete due to the low penetration of enzyme into some cell types. Many patients on ERT still develop progressing kidney and heart disease. There are other shortcomings of ERT, such as high cost, burden of life-long intravenous infusion, and allergic reaction to ERT. The limitations of ERT highlight the need for safe and effective small molecule therapies that are more efficient at penetrating diverse cell types and tissues.
AceLink is developing a GCS inhibitor AL01211 to treat Fabry disease.
© Copyright AceLink Therapeutics. All rights reserved
